How to make secondary revenue by converting steam to export-ready electrical power
Nanaimo Forest Products’ Harmac Mill is a progressive, employee-owned company that produces standard and specialty kraft pulps for domestic use and export. We designed their new turbine generator (G4) facilities within a number of constraints, including small available area for turbine hall footprint; variable and unpredictable underlying geotechnical conditions.
BUSINESS PROBLEM SOLVED
Monetize existing renewable fuel steam generation capacity by installing a new condensing steam turbine generator to convert thermal energy to green electrical power for export to the grid.[/acc_item]
TECHNICAL PROBLEM SOLVED
Design the new turbine generator (G4) facilities within a number of constraints: small available area for turbine hall footprint; variable and unpredictable underlying geotechnical conditions; aggressive startup schedule; limited budget; minimal interference with existing operation during construction; work with all stakeholders to develop an innovative, robust approach to maximize energy usage by recycling the waste heat from the new turbine condenser to the production process while ensuring sufficient process isolation to prevent upsets from cascading from one system to the other; stage design so that construction access is maintained as required by the equipment delivery schedule; develop strategies for turbine maintenance access within the limited area available.
WHAT WE DID
Thanks to a number of successful energy conservation projects, Harmac was able to significantly reduce the amount of steam heat required for its pulp production processes. Harmac produces most of its steam from renewable carbon neutral fuels: wood waste and black liquor. Harmac’s energy conservation initiatives made additional steam available for thermal power generation. Recognizing a secondary revenue business opportunity, Harmac selected the Temec Engineering Group to further develop the scope of the project, and to provide detail engineering and scheduling services for the new turbine facilities.
The new turbine was manufactured by General Electric Thermodyne in Le Creuset, France. The turbine was designed in response to heat and material balances prepared by Temec, which used estimates of pulp production steam requirements and financial models to determine the optimum size and best efficiency point for the new turbine.
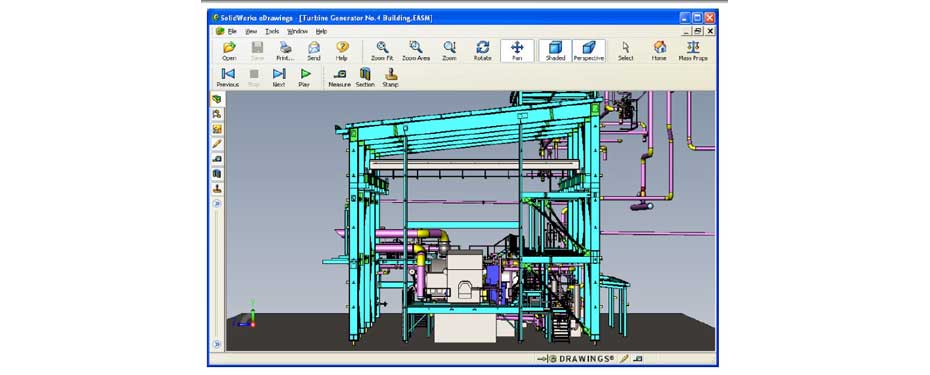
Following selection of the turbine, detail design and procurement started on the remaining parts of the project. A number of configuration options and locations for the new turbine hall were studied to determine the optimum initial and ongoing cost compromise for the new building: following this activity, an old maintenance shop was relocated and its existing building demolished to make way for the new turbine hall.
Engineering and construction was staged according to the project schedule so that the new facilities would be ready for delivery of the turbine and generator in early 2013. Delivery of other equipment items was carefully scheduled so that temporary access requirements for equipment installation could be integrated into the design.
The bridge crane delivery and installation were fast tracked so that the crane would be available to assist with construction activities. The steel frame was designed with removable sections to permit installation of the new condenser after the frame was complete, and to allow the new turbine to be brought in horizontally from the east end of the building to mate with the condenser already in place. A rotating application of the three dimensional design model was prepared to allow contractors and Harmac personnel to plan installation, operation and maintenance activities.
RESULTS
The staged approach to engineering, procurement and construction was very successful: in January 2013, the GE Thermodyne project manager remarked that, out of all the projects GE Thermodyne was building turbines for at the time, the only one that was ready to take delivery on schedule was the Harmac biomass fuelled power generation project.
The new facilities passed into the commissioning phase on schedule about eighteen months after a Letter of Intent was issued for the new turbine in December 2011, and the new turbine generator completed its 72 hour acceptance test in August 2013.
PROJECT LIFECYCLE SERVICES USED
| √ | Opportunity |
|
| √ | Definition |
|
| √ | Design |
|
| Fabrication | ||
| Construction | ||
| Start Up | ||
| In Service |